Psychology principles can be extremely useful in the process of designing and creating digital products. By understanding how people think, feel, and behave, designers and developers can create products that are more user-friendly, engaging, and effective. In this article, we’ll explore several key psychology principles that can be applied to digital product design, as well as specific techniques for using these principles to create great digital products.
Usability. Usability refers to how easy it is for users to understand and use a product. A product with high usability is intuitive, straightforward, and easy to learn, which can lead to increased user satisfaction and loyalty. To increase usability, designers can use techniques such as:

- Clear labeling: Use clear, descriptive labels for buttons, links, and other elements to make it easy for users to understand what they do.
- Consistency: This refers to the use of consistent language, layout, and design elements throughout the product. Consistency helps users understand and navigate the product more easily, as they can rely on familiar patterns and conventions.
- Intuitive navigation: Design the navigation of the product to be logical and easy to follow. Avoid using jargon or unnecessarily complex language.
- Simple instructions: Provide simple, step-by-step instructions for using the product, and avoid using complex or technical language.
- The “just-in-time” principle: Refers to providing users with enough information to complete tasks, but not too much information that it becomes overwhelming. Providing the right amount of information at the right time can help users understand and use the product more effectively.
- Feedback: It is important to provide users with feedback when they interact with the product. This can be through visual or audio cues, or through notifications or messages. Feedback helps users understand the results of their actions and can improve the overall usability of the product.
- Controllability: Controllability is a very important aspect of usability because it helps to create a sense of authority within the system, which makes the experience more enjoyable and efficient. When a user feels that they have control over the system, they are more likely to feel confident and motivated to use it. On the other hand, if a user feels that the system is not controllable, they may become frustrated or discouraged, which can lead to poor usability.
- Customizability: Also known as flexibility or adaptability, allows users to tailor the system or interface to their individual needs and preferences. Customizability can include options for changing the appearance, layout, or functionality of a system, as well as the ability to create and save personalized settings or profiles. A customizable interface may allow users to change the font size or color scheme to better suit their vision or accessibility needs, or to rearrange the layout of elements to make the interface more intuitive or efficient for their workflow.
- Fault Tolerance: Also known as “Error Handling” or “Error Tolerance” allows a system or interface to continue functioning effectively even when errors or problems occur. Error tolerance can be achieved through a variety of methods, such as providing clear and concise error messages, allowing users to undo or reverse actions that resulted in errors, or providing alternative options or workarounds when errors occur.
Persuasion: Persuasion refers to the use of techniques and strategies to influence the attitudes or behaviors of others. In the context of digital product design, persuasion can be used to encourage users to take certain actions, such as making a purchase or signing up for a service. To increase Persuasion, these six core principles by Robert Cialdini can be used in digital product design.
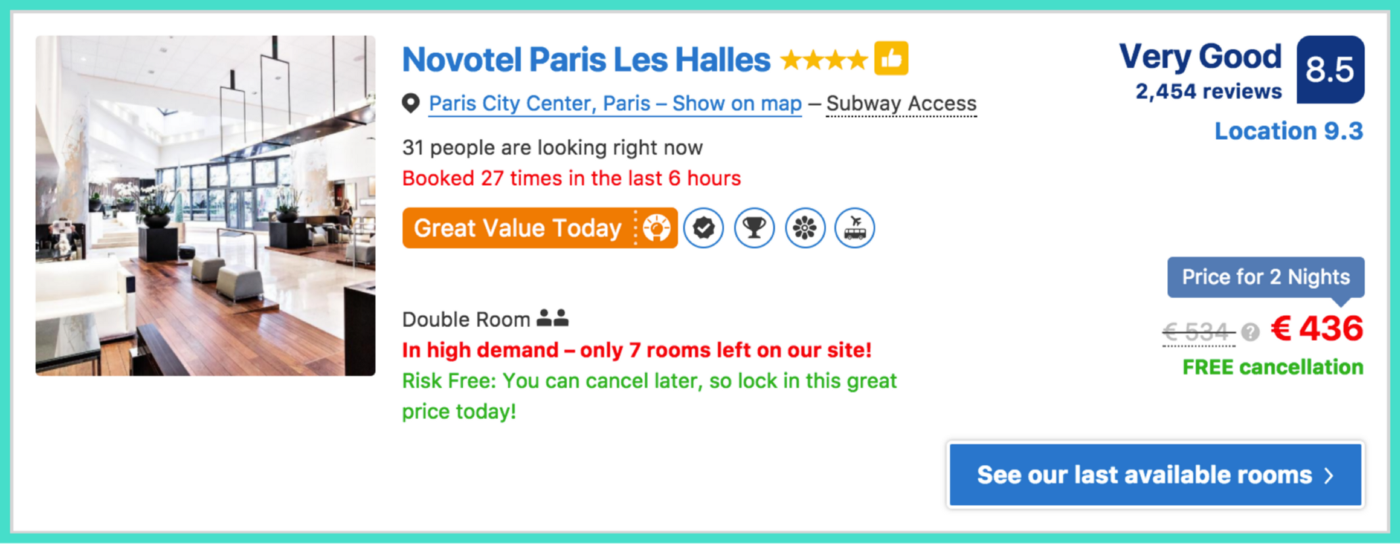
- Social proof: Showing that others are using the product can be a powerful way to persuade users to try it themselves. This can be done through customer testimonials, social media endorsements, or other forms of user-generated content.
- Scarcity: Creating a sense of urgency or limited availability can motivate users to act quickly. This can be done through techniques such as countdown timers, limited-time offers, or limited-edition products.
- Authority: Using credible sources to support the product can increase users’ trust and confidence in it. This can be done through expert endorsements, research studies, or other forms of third-party validation.
- Reciprocity: Reciprocity is a principle of persuasion that refers to the idea that people are more likely to comply with requests or favors if they feel that they have received something in return. This principle is based on the idea that people have a natural tendency to want to repay others for the things they have received, and that they feel a sense of obligation to do so.
- Commitment and Consistency : In product design, the principles of commitment and consistency can be used to increase the likelihood that users will continue to purchase or use a product. For example, offering a trial or free sample of a product can encourage users to make a small commitment that may lead to a larger commitment later on. Giving users the ability to customize or personalize a product can create a sense of ownership and commitment to the product. Consistently delivering high-quality products and experiences can build trust and establish a sense of consistency that may encourage users to continue using the product. Offering rewards or incentives for continued use of a product can create a sense of loyalty and encourage users to remain consistent in their use of the product.
- Liking: The principles of liking is used to create a positive emotional connection with users and increase the likelihood that they will purchase or use a product. e.g. People are often more likely to like products that are visually appealing and aesthetically pleasing. Products that align with the value or interests of the user may be more likeable. For example, a product that is eco-friendly or supports a cause that the user cares about may be more likeable to that user.
Motivation: The principles of Motivation can be used effectively in product design to create a sense of accomplishment and progress through the use of rewards, challenges, and feedback. For example, a digital product might offer rewards for completing certain tasks or challenges to encourage users to continue using it. Feedback, such as progress bars or notifications, can also help to keep users motivated by showing them their progress and accomplishments. Some ways that principles of motivation can be applied in product design include.
- Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: Designing interfaces that meet users’ basic physiological and safety needs, as well as their need for belongingness and self-esteem, can increase motivation to use the interface.
- Self-determination theory: Designing interfaces that allow users to feel a sense of autonomy, competence, and relatedness can increase motivation and satisfaction with the interface.
- Expectancy theory: Designing interfaces that make it clear to users how their efforts will lead to desired outcomes can increase motivation to use the interface.
- Goal-setting theory: Designing interfaces that allow users to set and work towards specific, challenging goals can increase motivation and engagement with the interface.
- Self-efficacy theory: Designing interfaces that give users the tools and resources they need to feel confident in their ability to use the interface effectively can increase motivation to use it.
- Flow theory: Designing interfaces that allow users to fully immerse themselves and become fully engaged in a task or activity can increase motivation and satisfaction with the interface.
User Engagement: Digital products that are engaging and enjoyable to use are more likely to be successful. Engaging products often have features that encourage exploration and offer a sense of accomplishment or progress. They may also offer personalised experiences and provide a sense of social connectedness. There are several principles that can be used to increase user engagement in product design:
- Make it easy to use: Designing products that are easy to use and understand can increase user engagement by reducing frustration and increasing satisfaction. This can be achieved through clear and intuitive navigation, consistent design patterns, and simple and straightforward instructions.
- Provide value: Designing products that provide value to users can increase user engagement by meeting their needs and helping them achieve their goals. This can be achieved through features and functionality that are relevant and useful to the user.
- Foster a sense of accomplishment: Designing products that allow users to set and work towards goals, and providing feedback and recognition for their progress, can increase user engagement by creating a sense of accomplishment and progress.
- Incorporate social features: Designing products with social features, such as the ability to share achievements or compete with friends, can increase user engagement by creating a sense of community and competition.
- Create a sense of personalisation: Designing products that allow users to customize and personalize their experience can increase user engagement by fostering a sense of ownership and connection to the product.
Understanding Specific Needs and Preferences: Understanding the specific needs and preferences of the target audience is crucial in product design, as it allows designers to create products that are tailored to the needs and preferences of the intended users. There are several ways that designers can identify the specific needs and preferences of the target audience, including:
- User Research: User research methods such as interviews, focus groups, and usability testing can provide valuable insights into the needs and preferences of the target audience.
- Analyzing Data: Analyzing data such as market research, customer feedback, and usage data can help designers understand the needs and preferences of the target audience.
- Consulting Experts: Consulting experts such as user experience designers, market researchers, or industry specialists can provide valuable insights into the needs and preferences of the target audience.
- Personas: Personas are fictional characters that represent the characteristics and needs of the target audience. Creating personas can help designers understand the specific needs and preferences of the target audience and design products that meet those needs.
Finally, it is important to continuously iterate and improve the design of digital products based on user feedback and data. By regularly updating and enhancing their products, creators can ensure that they meet the changing needs and preferences of their users.
In conclusion, the use of psychology principles can greatly contribute to the creation of great digital products. By considering usability, user engagement, persuasion, motivation, and the specific needs of the target audience, and continuously iterating and improving their designs, product creators can create digital products that are effective, engaging, and enjoyable to use.
